Introduction
Entrepreneurs are the brain of any business. They perform and wear multiple hats throughout the journey of a business. Being the owners of the firm, they cannot look to shy away from any responsibility, especially during the early stage when the manpower strength and available money to run the business is low. Entrepreneurship is not just about conceptualizing the business model, choosing a brand name, design of logo, and running of general day-to-day operations. Most business coaches and mentor would also scout for the importance of honing skills like leadership, communication. However, many tend to ignore a critical function – accounting. Accounting is essentially a language which depicts how well is a business been run. It is a way to numerically showcase your efficiency and control over the business. Even though unglamourous this function sounds, this is an essential activity to perform to run your business smoothly.
By accounting, it does not mean that every entrepreneur has to be a master at accounting standards, undergo a formal training or professional certification like Chartered Accountancy (CA). All what needs is a strong base of fundamentals of accounting.
Fundamentals of Accounting
Fundamentals of accounting is fairly uniformly applied across the globe. Fundamentals refer to some basic concepts, principles of accounting. Entrepreneurs with non-commerce background can quickly acquire them by going through this article and/or reading basic concepts freely available across internet.
4 Key Terms of Accounting:
- Asset – anything which you own and is expected to accrue benefits in future
- Liability – anything which you owe to others over both short and long term
- Expense – transactions where you pay money to purchase goods and/or services
- Income – transactions where you receive money to purchase goods and/or services
Golden Rules of Accounting:
- Debit what comes in and credit what goes out
- Credit the giver and debit the receiver
- Credit all income and debit all expenses
Basic Accounting Concepts: Accounting of transactions is performed using below underlying concepts.
- Entity concept – Identity of business is separate and distinct from its owners, promoters.
- Money measurement concept – Record only those transactions which can be measured in terms of money.
- Periodicity concept – Prepare accounting records and statements for every year period until existence.
- Accrual concept – Record transactions as and when they occur (not when cash is exchanged) and in the period to which they relate to.
- Matching concept – Record all related revenues and expenses of a transaction.
- Going concern concept – Underlying assumption that business will continue operation in foreseeable future.
- Cost concept – Determine value of asset based on historical/acquisition cost.
- Realisation concept – Any change in value of an asset is to be recorded only when realised.
- Dual aspect concept – Every transaction has two aspects, i.e., impacts one asset, liability, income and/or expense account.
- Conservatism – Refers to accounting for all future losses but not record future income.
- Consistency – To achieve comparability of the financial statements through time, the accounting policies should be consistently followed.
- Materiality – If the impact/effect is not considered to be material then it may be ignored.
Basic Accounting Assumptions: Below three concepts are fundamental assumptions to accounting which have to hold true under all circumstances, failing which there would be no proper accounting.
- Going Concern
- Consistency
- Accrual
Benefits
- Mastery over numbers – Knowing numbers related to your business should be at the back of fingertips for all entrepreneurs. Basic numbers like revenue, balance sheet size, gross profit margin, net profit is key to any financial discussions. Inability to recall these basic numbers can result in embarrassment in business meetings.
- Financial decision making – As owners of business, decision of an entrepreneur largely shapes the future of the business. In order to ensure a smooth sail, an entrepreneur’s decisions need to be financially sound not just based on gut feeling.
- Future planning – Accounting skills are required in every stage of business. Proper accounting helps you navigate vital business metrics like forecast revenues and profitability, required debt, probable tax outflow etc. With these numbers, an entrepreneur can plan for a brighter future.
- Effective communication with accounting team – Accounting policies vary across businesses and are framed based on management’s views, goals, and objectives. Hence, in order to create and follow an effective, consistent accounting policy, even an entrepreneur needs to be aware of fundamentals so that everyone is aligned with business goals and objectives.
Essential Accounting Skills
Having understood the fundamentals, and benefits of accounting, we will now dwell upon the top 8 accounting skills that are essential for any entrepreneur. Good knowledge of these skills would go a long way in helping being aware of current state of affairs of your business.
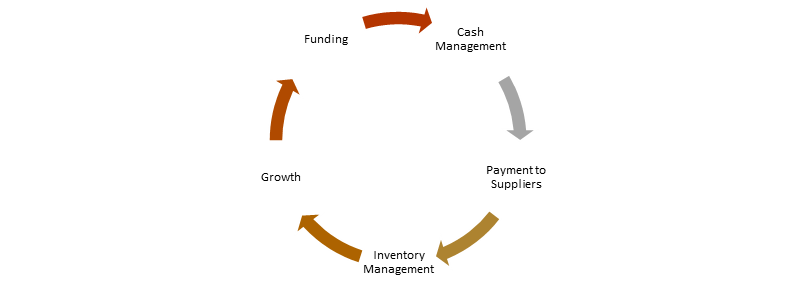
- Cash Flow Management – Revenue is vanity, Profit is sanity and Cash is KING – Alan Miltz is an evergreen quote to stress the importance of having this asset. Unavailability of this asset can mean closure of your business, both, in the short-term and long-term. Hence, it becomes vital to effectively monitor, track, and manage your cash flows. For entrepreneurs who start with limited capital and support, cash is the lifeline of your business. Its an oxygen that your business always needs to survive. Without cash, businesses fall under the vicious circle of living life at the edge, i.e., inability to pay suppliers/creditors leads to lack of inventory leading to lack of growth which translates into lower funding and valuation – refer below image for the cycle of cash management and its dependent flows.
- Balance Sheet Management – Balance Sheet is like a report card of your business which gives an instant view on the financial health of your business. Knowledgeable investors study this statement very minutely to understand the current state of affairs. On one hand, it shows the total assets owned by your business and on the other hand, shows money owed to lenders, suppliers, and creditors.
It will easily reflect the way a business is being run – whether its run-on credit or on cash, healthy basis. For example, generating higher turnover looks good on the income statement but a corresponding increase in the borrowers/debtors signals that value of sales is not being realized in cash and there runs a risk of customer default. Again, the investors do not just focus on the assets side. Keeping a constant check on the growing list of lenders/creditors is equally important to ensure long-term success.
- Profitability –Profit, commonly also referred as Income, means the net value of money left over from total sales/revenue after deducting all your expenses and taxes. This is a statement which shows if you are actually making any money from conducting this business or you are eroding capital and investor’s wealth. Although, the first metric to be seen in any business is revenue/turnover, however, seasoned investors are equally keen on seeing this number. Not everyone can start a business being profitable and thus initially may incur losses to create a market demand, acquire customers etc. However, these losses cannot continue forever for money in the bank will soon dry out and one may have to close down their dream – business.
- Projections – Nobody knows the business better than an entrepreneur. They are in a driver seat to plan, forecast and make projections of the future directions and path of the business. Having a projection of where the business will stand in short-term and long-term gives a good indication of well an entrepreneur is involved in the business. Projections about sales, cash flows, profitability, inventory are KPIs for any business.
- Inventory Management – Business is an act of providing/selling a good/service. Having sufficient inventory ensures you are able to meet the demands of the market and customers. In order to meet this demand, an entrepreneur must be aware on the inventory turnover ratio to effectively manage working capital.
- Expense Management – Effectively tracking your expense helps avoid the pitfall of unnecessary expenses. Although an entrepreneur may not track daily expense vouchers, but a knowledge of expense management can help keep effective checks on this daily, small but cash-linked area of business.
- Tax Obligations –It’s a myth that tax related obligations and payments arise only when you earn profit. Most of the laws across jurisdictions require businesses to periodically report their state of affairs, pay taxes on selling goods/services. In the absence of fulfilling these basic obligations, businesses might have to endure unnecessary, time-consuming trips to tax departments and pay hefty fines, penalties. Payment of such fines and penalties would be an additional burden and must be avoided at all costs.
- Distinguish between Fixed & Variable Costs – Understanding the difference between fixed and variable cost is key to determine the selling price of your good/service. Variable costs plus desired margin results in price to be charged, while fixed costs should not be considered. Fixed costs are immune to sales volume and are expected to remain same over a period of time. Costs like rent, insurance premium, interest payments are examples of fixed costs. On the other hand, variable costs are directly proportional to the sales volume achieved and hence, plays a huge role in unit economies of scale. Examples of variable costs would include direct labor, raw materials, logistic expenses.



